Introduction
Cảbon, a non-metallic element symbolized by “C” with an atomic number of 6, is nothing short of extraordinary. It exists in several forms and is fundamental to life as we know it. This blog post will guide you through the multifaceted world of carbon, revealing its significance, diverse forms, practical uses, environmental impact, and future innovations.
What Makes Carbon Special?
The Versatility of Carbon
Cảbon stands out due to its unique bonding capabilities. This element can form a staggering variety of compounds, making it the backbone of organic chemistry. Its ability to bond with itself and other elements enables the creation of complex molecules essential for life.
Carbon’s Role in Life
At a biological level, carbon forms the basis of essential molecules like proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. These molecules are crucial for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs.
Industrial Relevance
Beyond biology, carbon has a broad range of industrial applications. From the diamonds in your jewelry to the graphite in your pencils, Cảbon is everywhere. This versatility extends to many other fields, including technology and medicine.
Forms of Cảbon
Allotropes of Cảbon
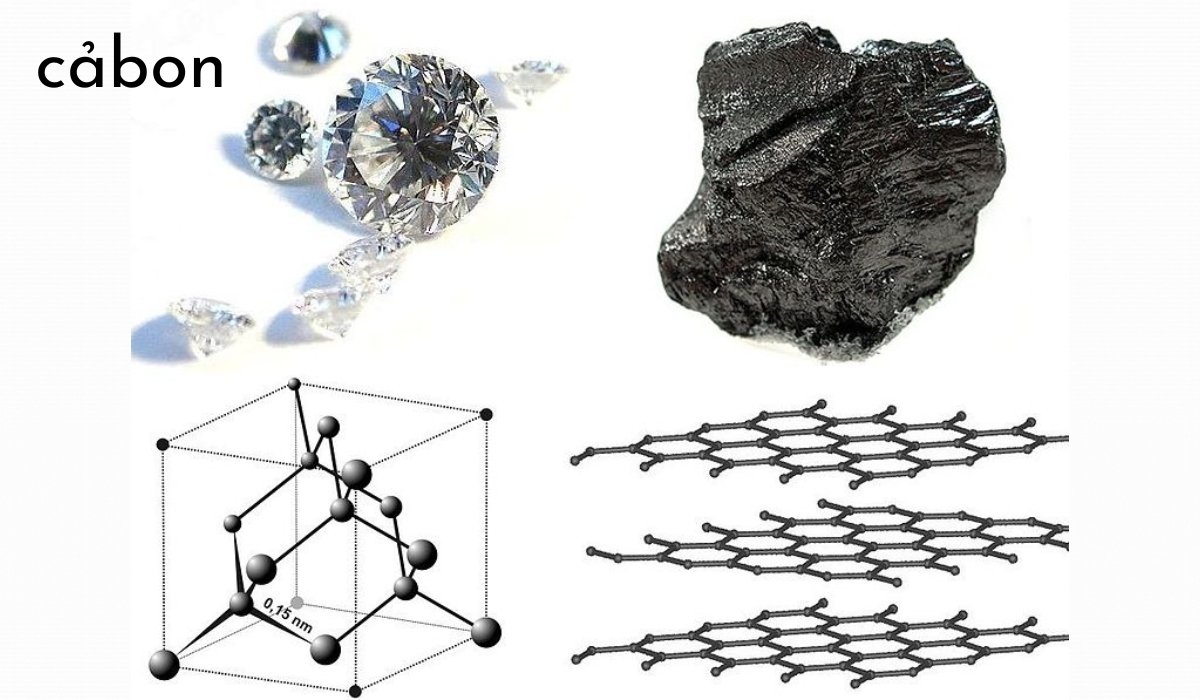
Diamond
Diamonds are the hardest natural materials and are prized for their brilliance and durability. Their crystalline structure makes them incredibly strong, leading to various applications in jewelry and cutting tools.
Graphite
In contrast to diamonds, graphite is soft and slippery. Its layered structure allows the layers to slide over each other, making it ideal for use in pencils. Graphite is also a good conductor of electricity, which makes it valuable in electronic applications.
Cảbon Nanotubes
Cảbon nanotubes are cylindrical structures that combine exceptional strength with electrical conductivity. These properties make them revolutionary in various industries, including electronics, material science, and even medicine.
Cảbon Compounds
Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are molecules that contain carbon atoms. These compounds are the foundation of all known life. They include carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, each playing a vital role in biological processes.
Inorganic Compounds
While less common than organic compounds, inorganic carbon compounds showcase the element’s versatility. Examples include carbon dioxide (CO2), a key player in the Earth’s Cảbon cycle, and carbonates, which are found in rocks and minerals.
Cảbon in Everyday Life
Food and Agriculture
Carbon plays a crucial role in agriculture through the carbon cycle. Plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis to produce glucose, which serves as food for humans and animals. This makes carbon an integral part of the food we consume daily.
Medicine
In the medical field, carbon compounds are indispensable. Many pharmaceuticals contain carbon atoms, and carbon-based materials are used in medical imaging and devices. For instance, activated Cảbon is used for detoxification and purification processes.
Technology
The tech industry benefits immensely from Cảbon. From the silicon carbide used in semiconductors to the graphite in batteries, carbon is a key component in many technological advancements. Cảbon fibers are also used in making lightweight, durable materials for aerospace and automotive industries.
Environmental Impact of Carbon
Carbon Footprint
Your carbon footprint is the total amount of greenhouse gases, including CO2, that your activities produce. Reducing your carbon footprint involves adopting practices that minimize these emissions, such as using energy-efficient appliances and reducing waste.
Carbon Emissions
The burning of fossil fuels is the primary source of carbon emissions. These emissions contribute to air pollution and climate change, posing severe risks to the environment and human health.
Global Warming
Excessive carbon emissions lead to global warming, a phenomenon where the Earth’s average temperature rises due to the greenhouse effect. This disrupts climate patterns, leading to extreme weather conditions and loss of biodiversity.
Sustainable Practices with Carbon
Carbon Capture
Carbon capture technologies aim to capture and store CO2 emissions before they reach the atmosphere. These technologies are essential in mitigating the environmental impact of carbon emissions and are increasingly being adopted in industrial settings.
Carbon Offsetting
Carbon offsetting involves compensating for your carbon emissions by funding projects that reduce CO2 in the atmosphere. This can include reforestation, renewable energy projects, and carbon capture initiatives.
Sustainable Technologies
The development of sustainable technologies focuses on reducing reliance on carbon-intensive practices. This includes renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, which emit little to no carbon during operation.
Industries and Carbon Management
Corporate Responsibility
Businesses are increasingly adopting carbon management practices to fulfill their social responsibility. This involves monitoring and reducing their carbon emissions and implementing sustainable practices across their operations.
Carbon Neutrality Initiatives
Carbon neutrality aims for zero net carbon emissions. Companies achieve this by balancing emitted CO2 with an equivalent amount of CO2 removal or offsetting. This emphasizes sustainability and responsible business practices.
Green Business Practices
Minimizing the carbon footprint involves adopting green business practices. This includes energy-efficient operations, sustainable sourcing, and waste reduction, all of which contribute to environmental stewardship.
Future Innovations in Carbon Use
Emerging Technologies
Research is uncovering new ways to utilize carbon in cutting-edge technologies. These include the development of carbon-neutral fuels and the use of carbon in advanced manufacturing processes.
Carbon-Based Materials
The development of advanced carbon-based materials, such as carbon composites, holds great promise for various industries. These materials are lightweight yet strong, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and construction applications.
Research and Development
Investments in research and development are driving innovations in carbon use. This includes exploring new applications for carbon nanotubes, graphene, and other advanced materials that can reshape the future of various industries.
Conclusion
Carbon is a ubiquitous element that impacts everything from biological processes to technological advancements. Understanding its various forms, applications, and environmental impact is crucial for making informed decisions in both personal and professional contexts. By adopting sustainable practices and staying informed about future innovations, we can ensure a balanced and sustainable future for generations to come.
You may also like: Imacion Revolutionizing Creativity and Innovation